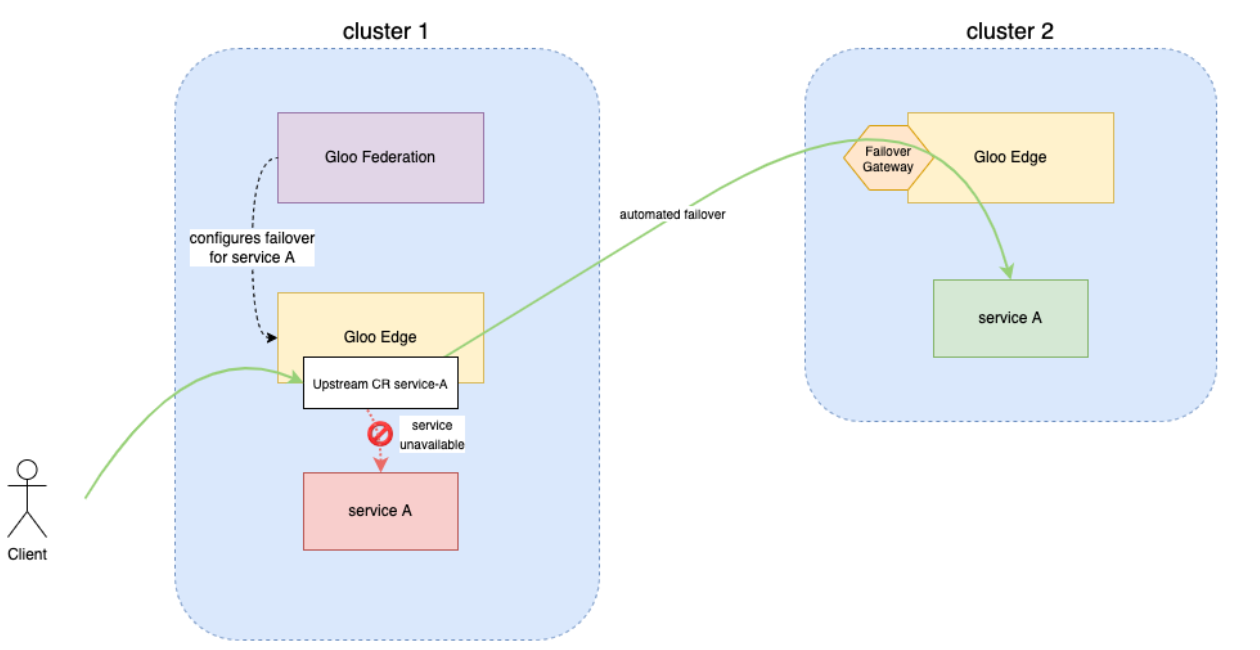
Service Failover
When an Upstream fails or becomes unhealthy, Gloo Gateway Federation can automatically fail traffic over to a different Gloo Gateway instance and Upstream. In this guide, you test this functionality by registering two clusters with Gloo Gateway Federation. Then, you create a Kubernetes service on each cluster and verify it is available as an Upstream. You create a FailoverScheme in Gloo Gateway Federation with one Upstream as the primary and the second as a backup. Finally, you simulate a failure of the primary Upstream and verify that the service fails over to the secondary.
Prerequisites
To successfully follow this Service Failover guide, make sure that you have the following command line tools.
kubectl- Execute commands against Kubernetes clustersglooctl- Register the Kubernetes clusters with Gloo Gateway Federationopenssl- Generate certificates to enable mTLS between multiple Gloo Gateway instances
You also need two Kubernetes clusters running Gloo Gateway Enterprise and an installation of Gloo Gateway Federation with both clusters registered. You can use kind to deploy local clusters on Docker, or select one of many other deployment options for Gloo Gateway on Kubernetes.
This example assumes two clusters, local and remote. The local cluster is also running Gloo Gateway Federation in addition to Gloo Gateway Enterprise. The kubectl context for the local cluster is gloo-fed and the remote cluster is gloo-fed-2.
Upgrading Gloo Gateway to use failover
Gloo Gateway Enterprise version 1.5.0-beta4 or later is required to use failover. You can enable failover by setting following Helm value: gloo.gatewayProxies.NAME.failover.enabled=true.
An example Helm override file for installing Gloo Gateway with failover is:
gloo:
gatewayProxies:
gatewayProxy:
failover:
enabled: true
An example helm command to upgrade Gloo Gateway is:
helm upgrade gloo glooe/gloo-ee --namespace gloo-system --values enable-failover.yaml
Configure Gloo Gateway for Failover
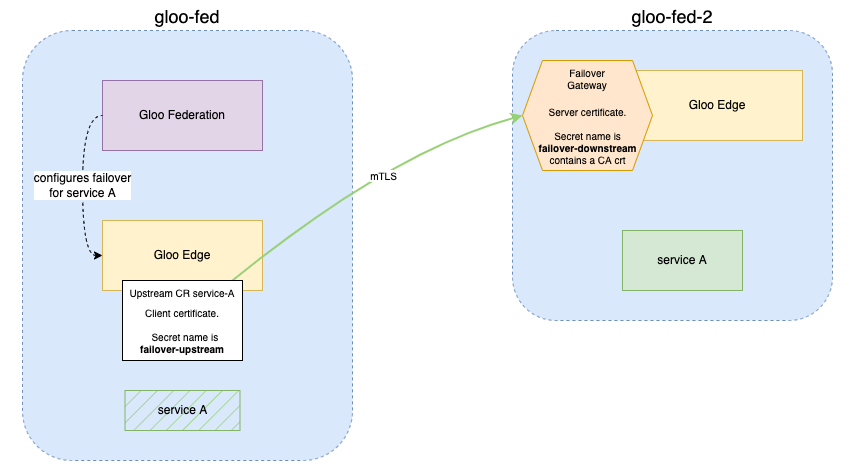
The first step to enabling failover is security. As failover allows communication between multiple clusters, it is crucial that the traffic be encrypted. Therefore certificates need to be provisioned and placed in the clusters to allow for mTLS between the Gloo Gateway instances running on separate clusters.
Create the certificates and secrets for mTLS
To enable mTLS, you need to create two distinct Kubernetes secrets containing x509 certificates:
- On the client side (the
gloo-fedcluster), the Upstream CR automatically uses a client certificate that is namedfailover-upstream. - On the server side (the
gloo-fed-2cluster), the Failover Gateway exposes a server certificate and also validates the client certificate with a CA cert (a truststore).
The following two commands generate all the necessary certificates.
# Generate downstream cert and key
openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 \
-keyout tls.key -out tls.crt -subj "/CN=solo.io"
# Generate upstream ca cert and key
openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 \
-keyout mtls.key -out mtls.crt -subj "/CN=solo.io"
Once the certificates have been generated, we can place them in the cluster as secrets so that Gloo Gateway can access them.
# Set the name of the local and remote cluster contexts
REMOTE_CLUSTER_CONTEXT=gloo-fed-2
LOCAL_CLUSTER_CONTEXT=gloo-fed
# Set context to remote cluster
kubectl config use-context $REMOTE_CLUSTER_CONTEXT
# Create the secret
glooctl create secret tls --name failover-downstream \
--certchain tls.crt --privatekey tls.key --rootca mtls.crt
# Set the context to the local cluster
kubectl config use-context $LOCAL_CLUSTER_CONTEXT
# Create the secret
glooctl create secret tls --name failover-upstream \
--certchain mtls.crt --privatekey mtls.key
Create the failover gateway
In order to use a Gloo Gateway Instance as a failover target it first needs to be configured with an additional listener to route incoming failover requests.
The Gateway resource below sets up a TCP proxy which is configured to terminate mTLS traffic from the primary Gloo Gateway instance, and forward the traffic based on the SNI name. The SNI name and routing are automatically handled by Gloo Gateway Federation, but the certificates are the ones created in the previous step.
The service creates an externally addressable way of communicating with the Gloo Gateway instance in question. This service may look different for different setups, in our example it is a LoadBalancer service on the specified port. If you are using clusters built with kind, you will need to use a NodePort service. Gloo Gateway Federation will automatically discover all external addresses for any Gloo Gateway instance.
The gateway and service below can also be created by setting the helm value for Gloo Gateway when installing:
gatewayProxies.NAME.failover.enabled=true.
# Set context to remote cluster
kubectl config use-context $REMOTE_CLUSTER_CONTEXT
# Apply failover gateway and service
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: gateway.solo.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: failover-gateway
namespace: gloo-system
labels:
app: gloo
spec:
bindAddress: "::"
bindPort: 15443
tcpGateway:
tcpHosts:
- name: failover
sslConfig:
secretRef:
name: failover-downstream
namespace: gloo-system
destination:
forwardSniClusterName: {}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: gloo
gateway-proxy-id: gateway-proxy
gloo: gateway-proxy
name: failover
namespace: gloo-system
spec:
ports:
- name: failover
nodePort: 32000
port: 15443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 15443
selector:
gateway-proxy: live
gateway-proxy-id: gateway-proxy
sessionAffinity: None
type: LoadBalancer
EOF
You can validate the service and gateway have deployed successfully using the following commands:
kubectl get gateway -n gloo-system failover-gateway
kubectl get svc -n gloo-system failover
Deploy our Sample Application
To demonstrate Gloo Gateway multi-cluster failover feature, we will create a relatively contrived example which can easily show off the power of the feature.
This application consists of two simple workloads which just return a color. The workload in the local cluster returns the color “blue”, and the workload in the remote cluster returns the color “green”. Each workload also has a healthcheck endpoint running at “/health” which can be manually made to fail for demonstration purposes.
The first step is to deploy the application to each cluster by running the following commands.
Create Local Color App (BLUE):
kubectl apply --context $LOCAL_CLUSTER_CONTEXT -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: bluegreen
text: blue
name: service-blue
namespace: default
spec:
ports:
- name: color
port: 10000
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 10000
selector:
app: bluegreen
text: blue
sessionAffinity: None
type: ClusterIP
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: bluegreen
text: blue
name: echo-blue
namespace: default
spec:
progressDeadlineSeconds: 600
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
app: bluegreen
text: blue
strategy:
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 25%
maxUnavailable: 25%
type: RollingUpdate
template:
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: bluegreen
text: blue
spec:
containers:
- args:
- -text="blue-pod"
image: hashicorp/http-echo@sha256:ba27d460cd1f22a1a4331bdf74f4fccbc025552357e8a3249c40ae216275de96
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: echo
resources: {}
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
- args:
- --config-yaml
- |2
node:
cluster: ingress
id: "ingress~for-testing"
metadata:
role: "default~proxy"
static_resources:
listeners:
- name: listener_0
address:
socket_address: { address: 0.0.0.0, port_value: 10000 }
filter_chains:
- filters:
- name: envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.network.http_connection_manager.v3.HttpConnectionManager
stat_prefix: ingress_http
codec_type: AUTO
route_config:
name: local_route
virtual_hosts:
- name: local_service
domains: ["*"]
routes:
- match: { prefix: "/" }
route: { cluster: some_service }
http_filters:
- name: envoy.filters.http.health_check
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.http.health_check.v3.HealthCheck
pass_through_mode: true
- name: envoy.filters.http.router
clusters:
- name: some_service
connect_timeout: 0.25s
type: STATIC
lb_policy: ROUND_ROBIN
load_assignment:
cluster_name: some_service
endpoints:
- lb_endpoints:
- endpoint:
address:
socket_address:
address: 0.0.0.0
port_value: 5678
admin:
access_log_path: /dev/null
address:
socket_address:
address: 0.0.0.0
port_value: 19000
- --disable-hot-restart
- --log-level
- debug
- --concurrency
- "1"
- --file-flush-interval-msec
- "10"
image: envoyproxy/envoy:v1.14.2
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: envoy
resources: {}
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
restartPolicy: Always
schedulerName: default-scheduler
securityContext: {}
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
EOF
Create Remote Color App (GREEN):
kubectl apply --context $REMOTE_CLUSTER_CONTEXT -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: bluegreen
name: service-green
namespace: default
spec:
ports:
- name: color
port: 10000
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 10000
selector:
app: bluegreen
text: green
sessionAffinity: None
type: ClusterIP
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: bluegreen
text: green
name: echo-green
namespace: default
spec:
progressDeadlineSeconds: 600
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
app: bluegreen
text: green
strategy:
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 25%
maxUnavailable: 25%
type: RollingUpdate
template:
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: bluegreen
text: green
spec:
containers:
- args:
- -text="green-pod"
image: hashicorp/http-echo@sha256:ba27d460cd1f22a1a4331bdf74f4fccbc025552357e8a3249c40ae216275de96
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: echo
resources: {}
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
- args:
- --config-yaml
- |2
node:
cluster: ingress
id: "ingress~for-testing"
metadata:
role: "default~proxy"
static_resources:
listeners:
- name: listener_0
address:
socket_address: { address: 0.0.0.0, port_value: 10000 }
filter_chains:
- filters:
- name: envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.network.http_connection_manager.v3.HttpConnectionManager
stat_prefix: ingress_http
codec_type: AUTO
route_config:
name: local_route
virtual_hosts:
- name: local_service
domains: ["*"]
routes:
- match: { prefix: "/" }
route: { cluster: some_service }
http_filters:
- name: envoy.filters.http.health_check
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.http.health_check.v3.HealthCheck
pass_through_mode: true
- name: envoy.filters.http.router
clusters:
- name: some_service
connect_timeout: 0.25s
type: STATIC
lb_policy: ROUND_ROBIN
load_assignment:
cluster_name: some_service
endpoints:
- lb_endpoints:
- endpoint:
address:
socket_address:
address: 0.0.0.0
port_value: 5678
admin:
access_log_path: /dev/null
address:
socket_address:
address: 0.0.0.0
port_value: 19000
- --disable-hot-restart
- --log-level
- debug
- --concurrency
- "1"
- --file-flush-interval-msec
- "10"
image: envoyproxy/envoy:v1.14.2
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: envoy
resources: {}
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
restartPolicy: Always
schedulerName: default-scheduler
securityContext: {}
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
EOF
Now that we have our two applications up and running, we can configure health checks and the failover resource.
Configure Failover Through Gloo Gateway Federation
A major part of failover is health checking. In order for Envoy to determine the state of the primary and failover endpoints, health checking must be enabled. In this section we will specify a health check for the Blue instance of the application and create the failover configuration.
First, let’s add health checks to the blue Upstream:
kubectl patch --context $LOCAL_CLUSTER_CONTEXT upstream -n gloo-system default-service-blue-10000 --type=merge -p "
spec:
healthChecks:
- timeout: 1s
interval: 1s
unhealthyThreshold: 1
healthyThreshold: 1
httpHealthCheck:
path: /health
"
Once health checking has been enabled we can go ahead and actually create our FailoverScheme resource. This is the Gloo Gateway Federation resource which will dynamically configure failover from one root Upstream, to a set of prioritized Upstreams.
We will create the FailoverScheme resource in the gloo-system namespace:
kubectl apply --context $LOCAL_CLUSTER_CONTEXT -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: fed.solo.io/v1
kind: FailoverScheme
metadata:
name: failover-scheme
namespace: gloo-system
spec:
failoverGroups:
- priorityGroup:
- cluster: remote
upstreams:
- name: default-service-green-10000
namespace: gloo-system
primary:
clusterName: local
name: default-service-blue-10000
namespace: gloo-system
EOF
Now we will add a simple route to the Blue Upstream in our local cluster.
# Make sure the context is set to the local cluster
kubectl config use-context $LOCAL_CLUSTER_CONTEXT
glooctl add route \
--path-prefix / \
--dest-name default-service-blue-10000
At this point we have the Blue Upstream published through the Envoy proxy in our local cluster. The Green Upstream in the remote cluster has been configured as a failover option. In the next section we will validate the Blue Upstream is responding, simulate a health check failure, and verify the failover works properly.
Test That Everything Works
First we will test that the Blue Upstream is responding to requests on the Envoy proxy.
# Get the proxy URL
PROXY_URL=$(glooctl proxy url)
curl -v $PROXY_URL
You should receive a response similar to the output below. Note the message is “blue-pod”.
* Rebuilt URL to: http://52.234.106.206:80/
* Trying 52.234.106.206...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to 52.234.106.206 (52.234.106.206) port 80 (#0)
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> Host: 52.234.106.206
> User-Agent: curl/7.58.0
> Accept: */*
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< x-app-name: http-echo
< x-app-version: 0.2.3
< date: Tue, 21 Jul 2020 18:24:29 GMT
< content-length: 11
< content-type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
< x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 2
< x-envoy-upstream-healthchecked-cluster: ingress
< server: envoy
<
"blue-pod"
* Connection #0 to host 52.234.106.206 left intact
The Blue Upstream is responding to requests. Now we will force the Blue Upstream to fail its health check, thereby forcing a failover to the Green Upstream. We will do that by making a POST request on port 19000 to the echo-blue deployment.
# run in background using &
kubectl port-forward deploy/echo-blue 19000 &
curl -v -X POST http://localhost:19000/healthcheck/fail
The response should be a 200 OK from the healthcheck endpoint.
Now we will test the route again to make sure it is serving content from the Green Upstream instead.
curl -v $PROXY_URL
You should see the following output. Note the message is “green-pod” instead of “blue-pod” now.
* Rebuilt URL to: http://52.154.156.176:80/
* Trying 52.154.156.176...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to 52.154.156.176 (52.154.156.176) port 80 (#0)
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> Host: 52.154.156.176
> User-Agent: curl/7.58.0
> Accept: */*
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< x-app-name: http-echo
< x-app-version: 0.2.3
< date: Wed, 22 Jul 2020 00:54:39 GMT
< content-length: 12
< content-type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
< x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 4
< x-envoy-upstream-healthchecked-cluster: ingress
< server: envoy
<
"green-pod"
* Connection #0 to host 52.154.156.176 left intact
You can switch between the two services by enabling and disabling the Blue Upstream service using the following commands:
# Disable blue upstream
curl -v -X POST http://localhost:19000/healthcheck/fail
# Enable blue upstream
curl -v -X POST http://localhost:19000/healthcheck/ok
Cleanup
You may want to clean up the resources deployed during this guide. Run the following commands to remove the resources:
# Remove the FailoverScheme
kubectl delete failoverscheme -n gloo-system failover-scheme --context $LOCAL_CLUSTER_CONTEXT
# Remove the Blue Deployment
kubectl delete deployment echo-blue --context $LOCAL_CLUSTER_CONTEXT
kubectl delete svc service-blue --context $LOCAL_CLUSTER_CONTEXT
# Remove the Green Deployment
kubectl delete deployment echo-green --context $REMOTE_CLUSTER_CONTEXT
kubectl delete svc service-green --context $REMOTE_CLUSTER_CONTEXT
# Remove the Failover Gateway
kubectl delete -n gloo-system service/failover --context $REMOTE_CLUSTER_CONTEXT
kubectl delete gateway -n gloo-system failover-gateway --context $REMOTE_CLUSTER_CONTEXT
# Remove the secrets
kubectl delete secret tls --name failover-downstream --context $REMOTE_CLUSTER_CONTEXT
kubectl delete secret tls --name failover-upstream --context $LOCAL_CLUSTER_CONTEXT
Next Steps
Gloo Gateway Federation enables configurations to be applied across multiple clusters. You can learn more by following the Federation Configuration guide. We also recommend reading up about some of the concepts used by Gloo Gateway Federation.
