Additional Authorization servers (Enterprise)
Gloo Gateway Enterprise comes with an External Authorization service, with full-featured security policies, like OpenID Connect, Open Policy Agent, OAuth 2 scopes and a few more. Also, using the so-called passthrough system, you can extend the authorization logic and call your own authentication or authorization service.
There are certain cases where it’s more relevant to directly plug the ext_authz Envoy filter to your own authorization service. This article describes how to configure such connections between the Envoy data-plane and third-party authorization services.
Calling an external authorization service
Say you are running a corporate access management service that is in charge of returning new claims, like the role of the user who is authenticated.
With Gloo Gateway Enterprise, you can call the external service in two, non-exclusive ways, as shown in the following figure.
- Option A: use the Passthrough Auth plug-in, which comes with all the ExtAuth options (see
AuthConfig > passthrough) - Option B: define an additional ExtAuth server with the
namedExtAuthsetting, and call the additional ExtAuth server on the routes of your choice

In the first option, the connection has an extra network hop, but you can use the AuthConfig CR and more easily pass information between the authentication and authorization steps. For more information, see the gRPC Passthrough Auth guide.
Option A - Using the passthrough system
With Option A, you can compose your authentication and authorization workflow with the AuthConfig Custom Resource.
For instance, you can have a block that leverages the built-in OpenID Connect plug-in and another block where you define how to call your external authorization service.
The following diagram depicts a common use case wherein Gloo:
- uses OIDC to authenticate the end user
- uses the passthrough system to populate the request with an additional JWT, having authorization-centered claims (roles, etc.)
- uses the JWT policy to verify the signature of the newly created JWT
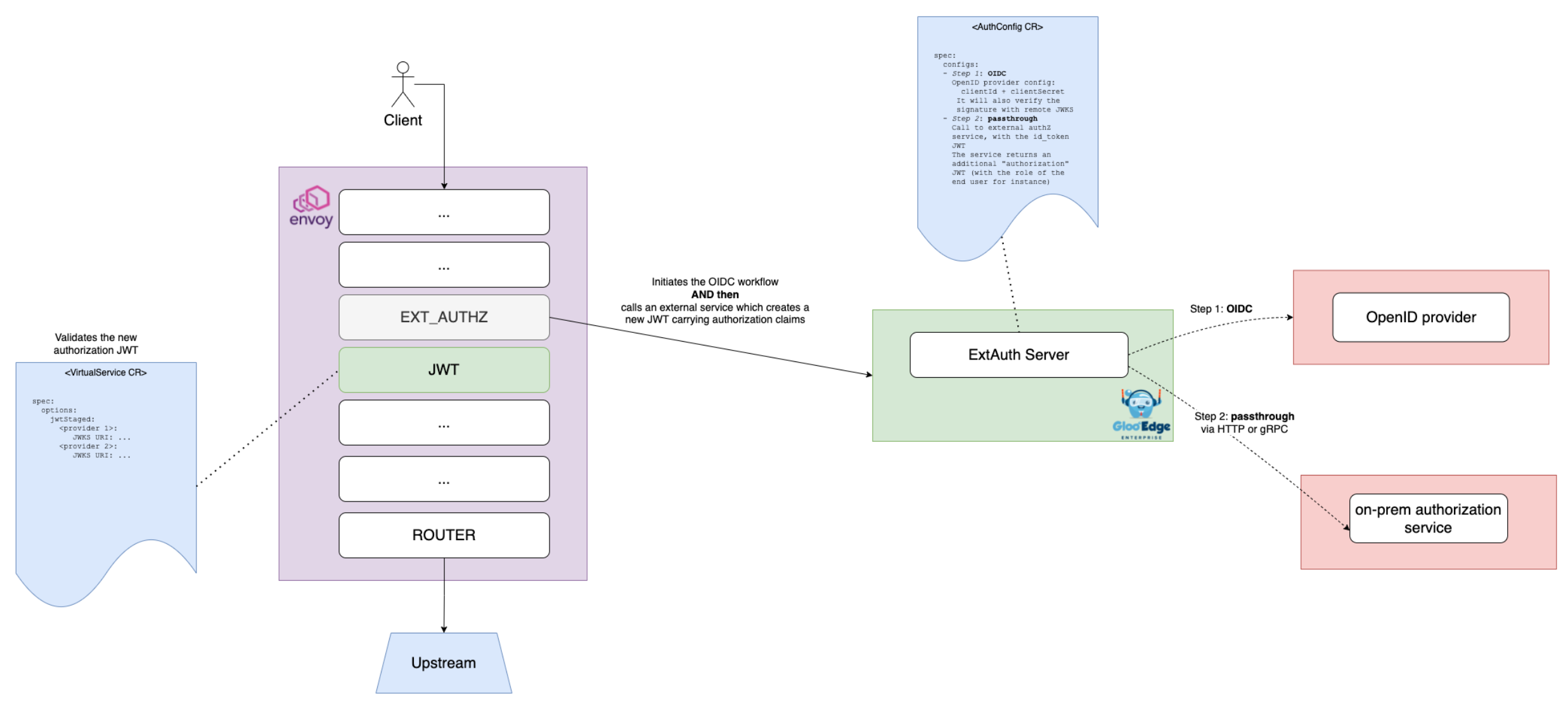
Also, note you can pass values between the AuthConfig blocks using the State map. More info in this section.
You can use either the gRPC Passthrough Auth protocol or HTTP Passthrough Auth.
Option B - Using namedExtAuth
In Gloo Gateway Enterprise, you can define additional ExtAuthZ servers in the Gloo Gateway settings.
For that, you must register your authorization servers in the “default” Settings custom resource, as shown in the following example. For more information, see the API reference.
kubectl -n gloo-system patch st/default --type merge -p "
spec:
extauth:
extauthzServerRef:
name: extauth
namespace: gloo-system
transportApiVersion: V3
userIdHeader: x-user-id
namedExtauth:
customHttpAuthz: # custom name
extauthzServerRef: # define where is running the third-party authorization server
name: default-http-echo-8080 # this is an Upstream CR. You must create it.
namespace: gloo-system
httpService: # this option enables communication over HTTP instead of gRPC (which is the default)
pathPrefix: /
"A more advanced use case is shown in the schema below. There are two additional ExtAuth services added to Gloo’s configuration.
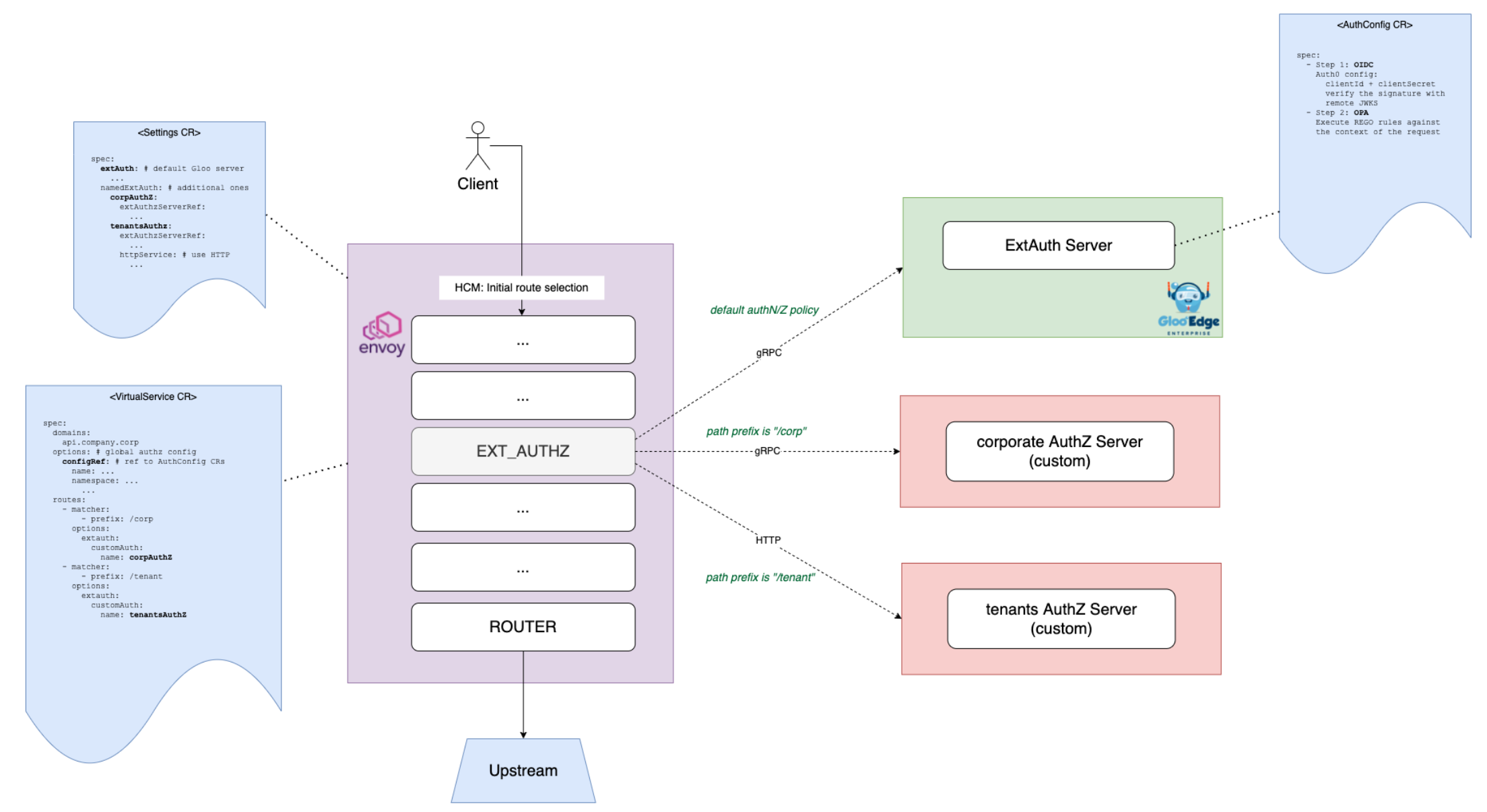
Gloo users can decide which ExtAuth service they want to call on a per-route level, using customAuth.
Example:
apiVersion: gateway.solo.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: httpbin
namespace: gloo-system
spec:
virtualHost:
domains:
- '*'
routes:
- matchers:
- prefix: /
routeAction:
single:
upstream:
name: default-httpbin-8000
namespace: gloo-system
options:
extauth:
customAuth: # set the authorization system at the route level
name: customHttpAuthz # one of the `namedExtAuth` The gRPC specification
For both the Passthrough Auth option and the namedExtAuth option, you must conform to the Envoy specification for the external Authorization service. For more information, see the following resources.
Managing headers
You can add new headers to the request from your external authorization service.
gRPC mode
For gRPC, use the protobuf specification and populate the OkHttpResponse with the new headers. The new headers are visible to the rest of the filter chain and are passed to the upstream service. For more information, see Sharing state with other auth steps.
HTTP mode
With both the HTTP passthrough option and the namedExtAuth with HTTP option, if you want to send new headers to the rest of the filter chain or to the upstream service, then just add the headers to the authorization response. Then, the headers are merged into the original request before being forwarded upstream.
You also decide which headers are allowed to go upstream and which are not. Under the httpService option, you can define some rules about headers you want to forward to the external authorization service, and also rules to sanitize headers before forwarding the request upstream.
